H1 Robot Tutorial

Humanoid Robot H1 Typing |

Humanoid Robot H1 Playing Piano |

Humanoid Robot H1 Playing Tennis |
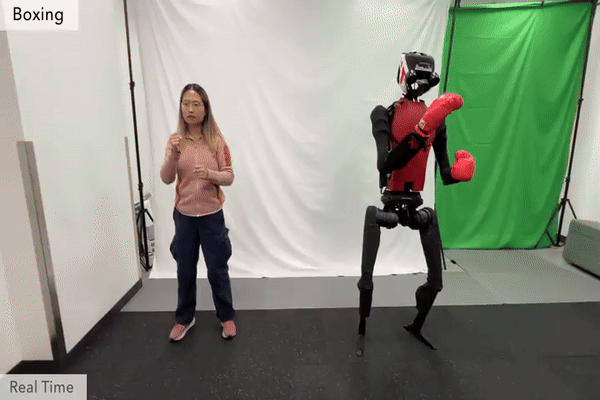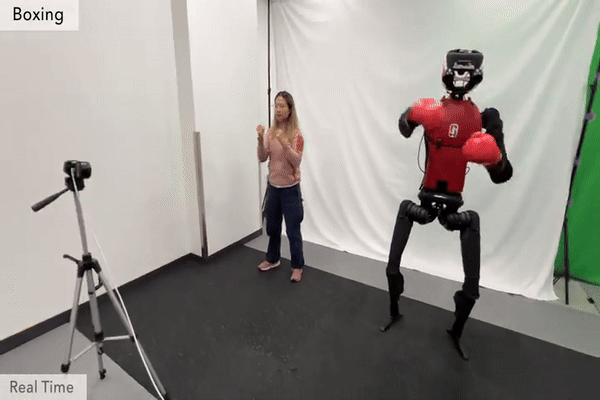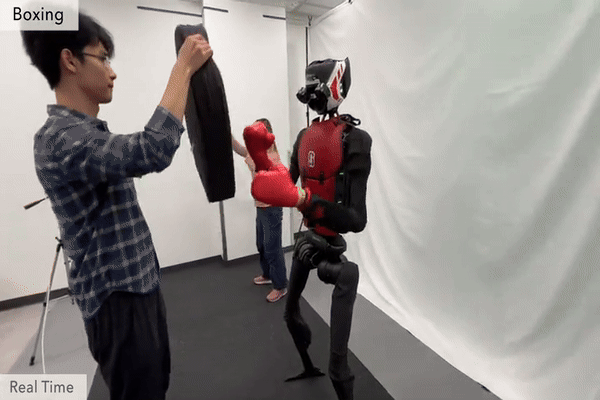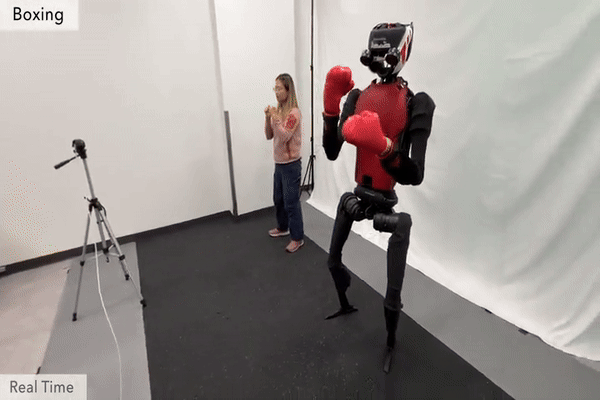
Humanoid Robot H1 Boxing |
Important
Please note that the content showcased here represents the individual achievements of Humanoid AI and Omni Human-to-Humanoid, and there has been no collaboration between them and our organization. The videos and gifs included on this page are intended strictly for educational and demonstrative purposes.
The provided tutorial will assist you with setting up and operating your H1 bi-pedal robot. The tutorial topics are listed in the left column and presented in the suggested reading order.
Insights from Leading Researchers
We are excited to highlight the innovative work presented on Humanoid AI and Omni Human-to-Humanoid. The researchers on Humanoid AI have developed a comprehensive system enabling humanoid robots to learn motion and autonomous skills from human data. Their approach involves training low-level policies in simulation through reinforcement learning using extensive human motion datasets. These policies allow humanoid robots to shadow human movements in real-time using only an RGB camera. The collected data is then used for supervised behavior cloning, enabling robots to autonomously perform various tasks such as wearing shoes, unloading objects, and interacting with other robots with impressive success rates. On the other hand, the work on Omni Human-to-Humanoid has resulted in OmniH2O, a versatile system for whole-body humanoid teleoperation and autonomy. By using kinematic poses as a universal control interface, OmniH2O allows humans to control humanoids through VR, verbal instructions, and RGB cameras. They have also integrated advanced models like GPT-4 to enable full autonomy. Their RL-based sim-to-real pipeline and the release of the OmniH2O-6 dataset highlight their contributions to humanoid skill learning.
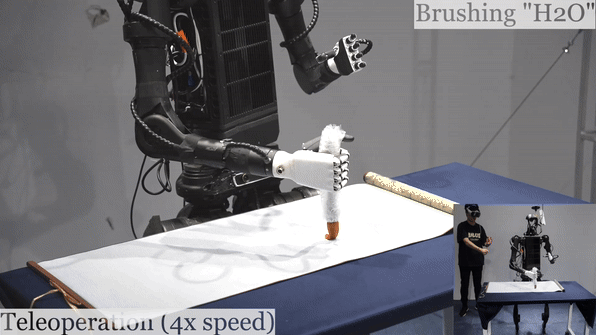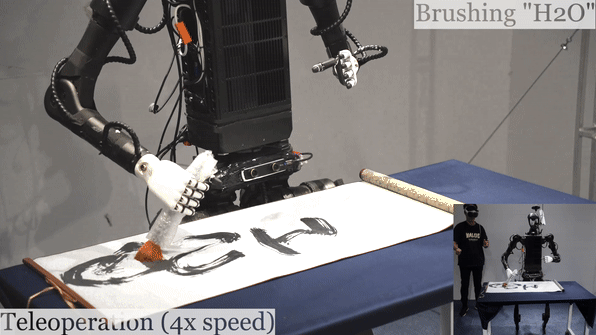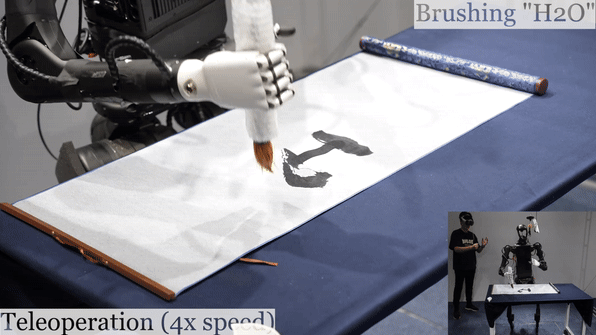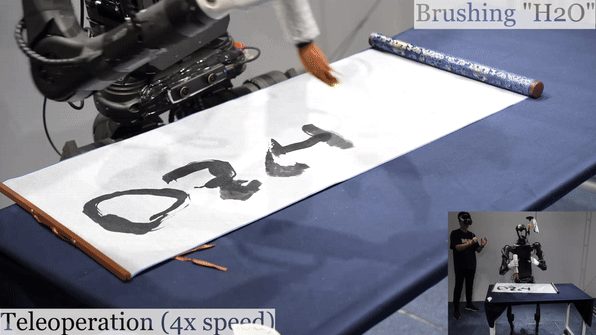
Humanoid Robot H1 Brush Teleoperation |
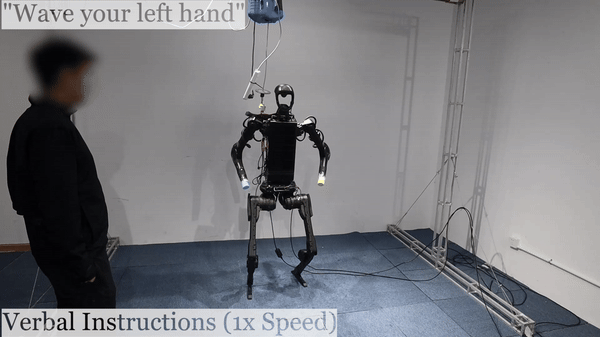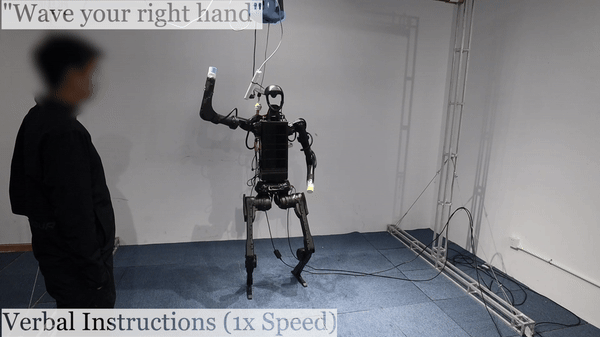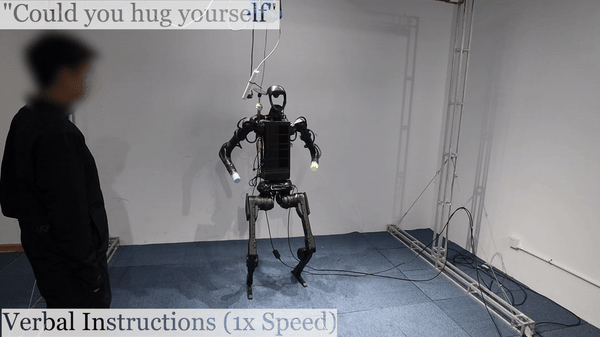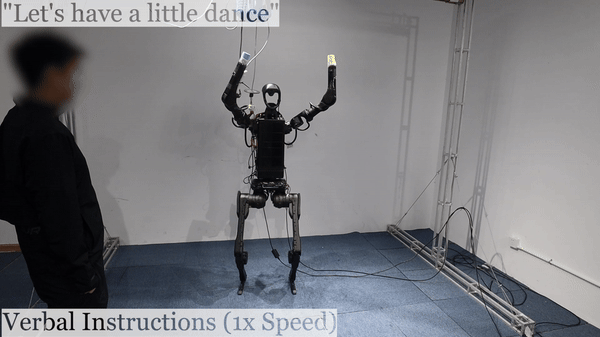
Humanoid Robot H1 Verbal Instructions |
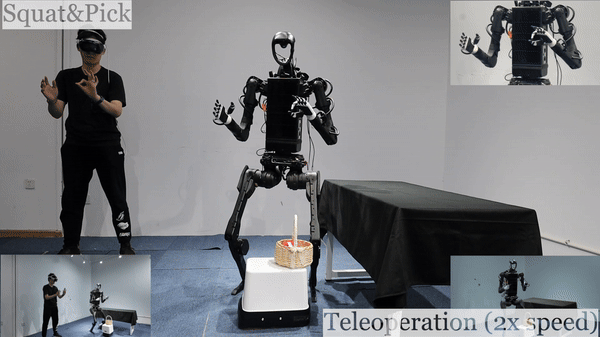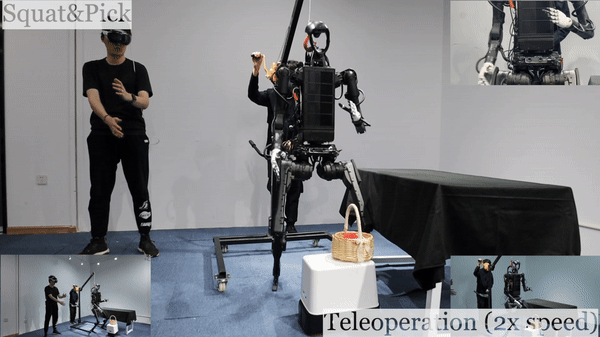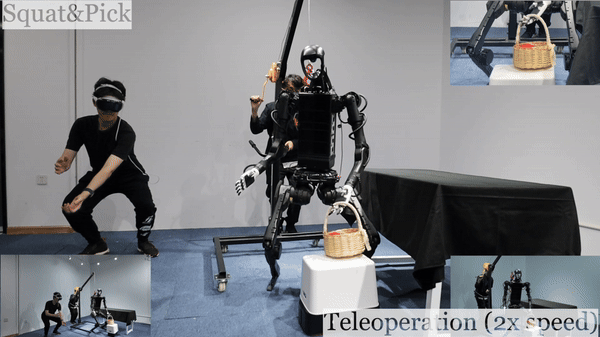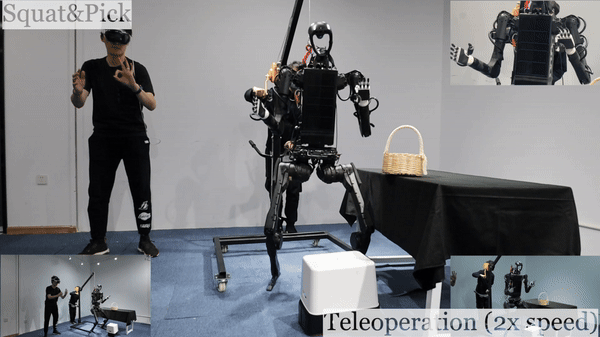
Humanoid Robot H1 Squat & Pick Basket |
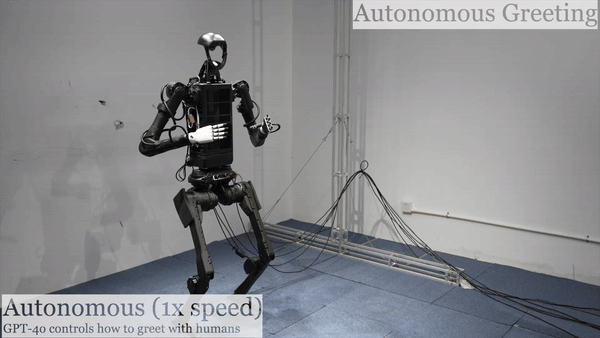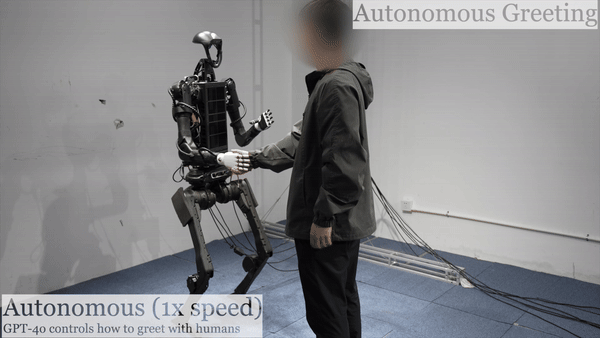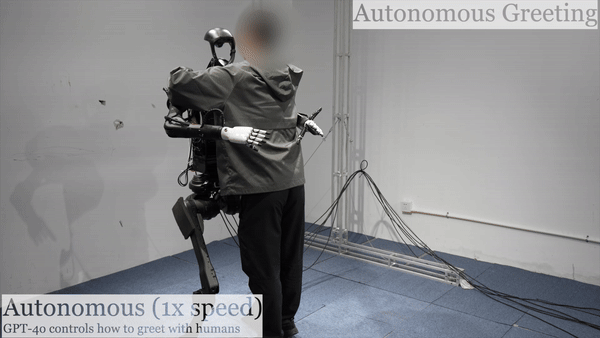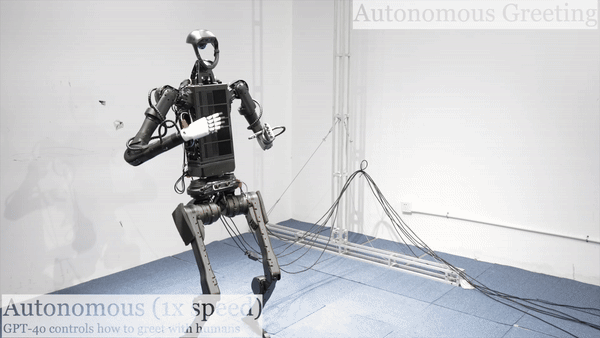
Humanoid Robot H1 GPT4o-Autonomous Greeting |
Warm Tips for Unitree Humanoid Robot Development and Usage
To align with the public’s preference for natural human-like movements, it’s important to adhere to these guidelines, particularly when filming humanoid robots:
Strive for upright or nearly upright knee joint positions when developing leg movement programs.
Reduce step frequency and minimize stationary stepping.
Keep the feet slightly close together during walking to maintain natural movement.
These tips are intended to enhance the authenticity of humanoid robot movements, especially in video documentation.